Express.js quickstart
Build a production-ready Express.js MCP server with TypeScript, custom middleware for OAuth token validation, and Scalekit authentication.
This guide shows you how to build a production-ready Express.js MCP server with TypeScript and Scalekit’s OAuth authentication. You’ll implement custom middleware for token validation, expose OAuth resource metadata for client discovery, and create MCP tools that enforce authorization using the MCP SDK.
Use this quickstart when you’re building Node.js-based MCP servers and want fine-grained control over request handling. The Express integration gives you flexibility to add custom routes, middleware chains, integrate with existing Express applications, and handle complex authorization requirements. The full code is available on GitHub.
Prerequisites
- A Scalekit account with permission to manage MCP servers
- Node.js 20+ installed locally
- Familiarity with Express.js, TypeScript, and OAuth token validation
- Basic understanding of MCP server architecture
Review the Express.js MCP authorization flow
-
Register your MCP server in Scalekit
Section titled “Register your MCP server in Scalekit”Create a protected resource entry so Scalekit can issue tokens that your custom Express middleware validates.
- Navigate to Dashboard > MCP Servers > Add MCP Server.
- Enter a descriptive name (for example,
Greeting MCP). - Set Server URL to
http://localhost:3002/(keep the trailing slash). - Click Save to create the server.
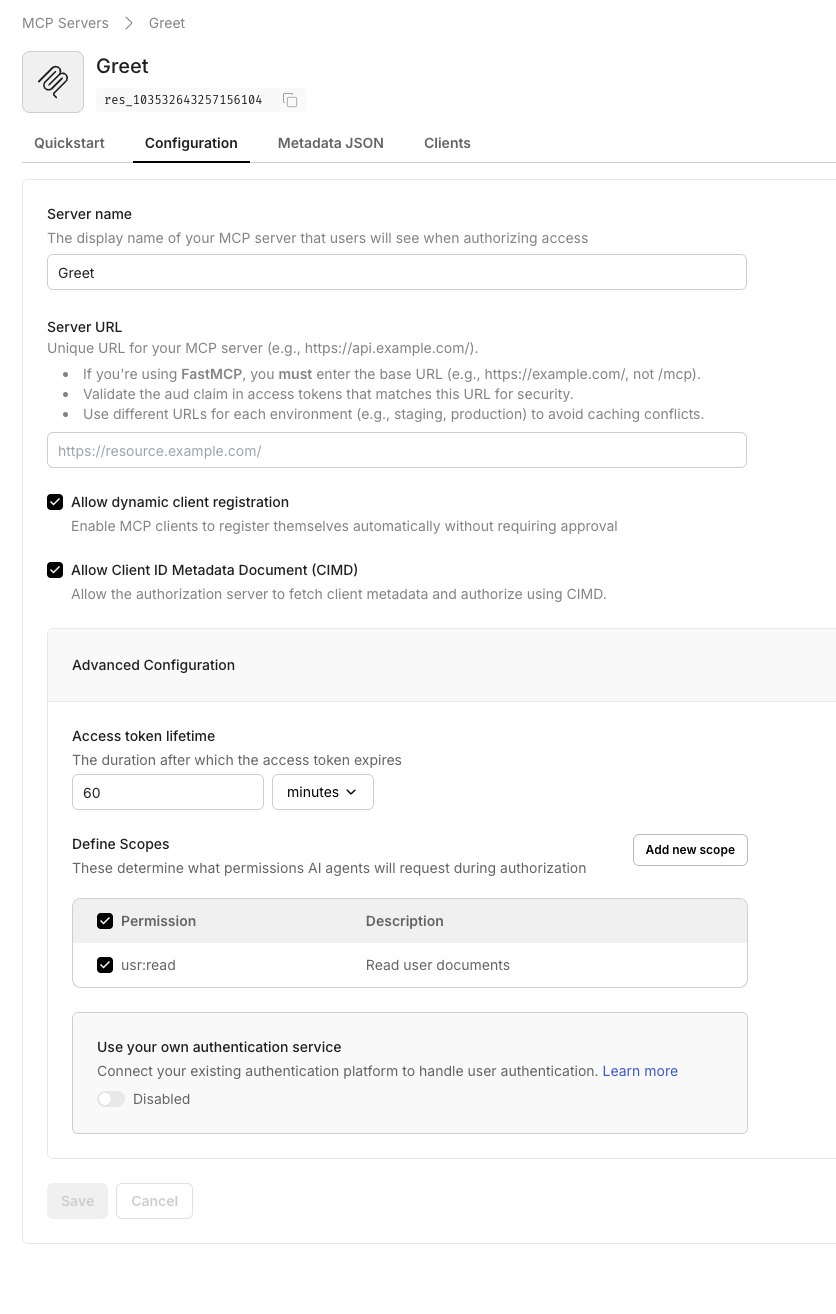
When you save, Scalekit displays the OAuth-protected resource metadata. Copy this JSON—you’ll use it in your
.envfile.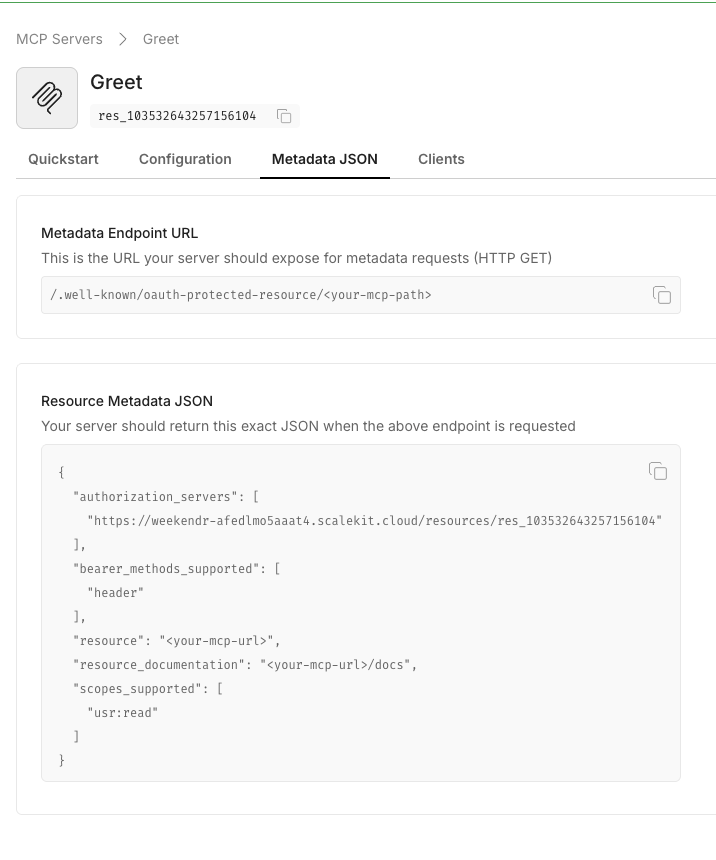
-
Create your project directory
Section titled “Create your project directory”Set up a clean directory structure for your TypeScript Express project.
Terminal mkdir express-mcp-nodecd express-mcp-node -
Add package dependencies
Section titled “Add package dependencies”Create a
package.jsonwith scripts and all required dependencies for Express, TypeScript, and the MCP SDK.Terminal cat <<'EOF' > package.json{"name": "express-mcp-node","version": "1.0.0","type": "module","scripts": {"dev": "tsx src/server.ts","build": "tsc","start": "node dist/server.js"},"dependencies": {"@modelcontextprotocol/sdk": "^1.13.0","@scalekit-sdk/node": "^2.0.1","cors": "^2.8.5","dotenv": "^16.4.5","express": "^5.1.0","zod": "^3.25.57"},"devDependencies": {"@types/cors": "^2.8.19","@types/express": "^4.17.21","@types/node": "^20.11.19","tsx": "^4.7.0","typescript": "^5.4.5"}}EOF -
Configure TypeScript
Section titled “Configure TypeScript”Add a TypeScript configuration file optimized for ES2022 modules and strict type checking.
Terminal cat <<'EOF' > tsconfig.json{"compilerOptions": {"target": "ES2022","module": "ES2022","moduleResolution": "node","esModuleInterop": true,"forceConsistentCasingInFileNames": true,"strict": false,"skipLibCheck": true,"resolveJsonModule": true,"outDir": "dist","rootDir": "src","types": ["node"]},"include": ["src/**/*"]}EOF -
Install dependencies
Section titled “Install dependencies”Install all packages declared in
package.json.Terminal npm install -
Configure environment variables
Section titled “Configure environment variables”Create a
.envfile with your Scalekit credentials and the protected resource metadata from step 1.Terminal cat <<'EOF' > .envPORT=3002SK_ENV_URL=https://<your-env>.scalekit.comSK_CLIENT_ID=<your-client-id>SK_CLIENT_SECRET=<your-client-secret>MCP_SERVER_ID=<mcp-server-id-from-dashboard>PROTECTED_RESOURCE_METADATA='<resource-metadata-json>'EXPECTED_AUDIENCE=http://localhost:3002/EOFopen .envVariable Description PORTLocal port for the Express server. Must match the Server URL registered in Scalekit (defaults to 3002).SK_ENV_URLYour Scalekit environment URL from Dashboard > Settings > API Credentials SK_CLIENT_IDClient ID from Dashboard > Settings > API Credentials. Used with SK_CLIENT_SECRETto initialize the SDK.SK_CLIENT_SECRETClient secret from Dashboard > Settings > API Credentials. Keep this secret and rotate regularly. MCP_SERVER_IDThe MCP server ID from Dashboard > MCP Servers. Not directly used in this implementation but documented for reference. PROTECTED_RESOURCE_METADATAThe complete OAuth resource metadata JSON from step 1. Clients use this to discover authorization requirements. EXPECTED_AUDIENCEThe audience value that tokens must include. Should match your server’s public URL (e.g., http://localhost:3002/). -
Implement the Express MCP server
Section titled “Implement the Express MCP server”Create
src/server.tswith the complete server implementation. This includes the Scalekit client initialization, authentication middleware for token validation, CORS configuration, and the greeting MCP tool.src/server.ts 6 collapsed linesimport 'dotenv/config';import cors from 'cors';import express, { NextFunction, Request, Response } from 'express';import { z } from 'zod';import { McpServer } from '@modelcontextprotocol/sdk/server/mcp.js';import { StreamableHTTPServerTransport } from '@modelcontextprotocol/sdk/server/streamableHttp.js';import { Scalekit } from '@scalekit-sdk/node';// Load environment variablesconst PORT = Number(process.env.PORT ?? 3002);const SK_ENV_URL = process.env.SK_ENV_URL ?? '';const SK_CLIENT_ID = process.env.SK_CLIENT_ID ?? '';const SK_CLIENT_SECRET = process.env.SK_CLIENT_SECRET ?? '';const EXPECTED_AUDIENCE = process.env.EXPECTED_AUDIENCE ?? '';const PROTECTED_RESOURCE_METADATA = process.env.PROTECTED_RESOURCE_METADATA ?? '';// Use case: Configure OAuth resource metadata URL for MCP clients// This allows MCP clients to discover authorization requirements via WWW-Authenticate header// Security: The WWW-Authenticate header signals to clients where to obtain tokensconst RESOURCE_METADATA_URL = `http://localhost:${PORT}/.well-known/oauth-protected-resource`;// WWW-Authenticate header for 401 responsesconst WWW_HEADER_KEY = 'WWW-Authenticate';const WWW_HEADER_VALUE = `Bearer realm="OAuth", resource_metadata="${RESOURCE_METADATA_URL}"`;// Initialize Scalekit client for token validation// Security: Use SDK to validate JWT signatures and claims// This prevents accepting forged or tampered tokensconst scalekit = new Scalekit(SK_ENV_URL, SK_CLIENT_ID, SK_CLIENT_SECRET);// Initialize MCP server with greeting tool// Context: The McpServer handles MCP protocol details while Express handles HTTP routingconst server = new McpServer({ name: 'Greeting MCP', version: '1.0.0' });// Use case: Simple greeting tool demonstrating OAuth-protected MCP operations// Context: This tool is protected by the authentication middleware applied to all routesserver.tool('greet_user','Greets the user with a personalized message.',{name: z.string().min(1, 'Name is required'),},async ({ name }: { name: string }) => ({content: [{type: 'text',text: `Hi ${name}, welcome to Scalekit!`}]}));// Initialize Express applicationconst app = express();// Enable CORS for cross-origin MCP clients// Use case: Allow MCP clients from different origins to connectapp.use(cors({ origin: true, credentials: false }));// Parse JSON request bodies// Context: MCP protocol uses JSON-RPC formatapp.use(express.json());// Use case: Expose OAuth resource metadata for MCP client discovery// This endpoint allows clients to discover authorization requirements and server capabilities// Context: MCP clients use this metadata to initiate the OAuth flowapp.get('/.well-known/oauth-protected-resource', (_req: Request, res: Response) => {if (!PROTECTED_RESOURCE_METADATA) {res.status(500).json({ error: 'PROTECTED_RESOURCE_METADATA config missing' });return;}const metadata = JSON.parse(PROTECTED_RESOURCE_METADATA);res.type('application/json').send(JSON.stringify(metadata, null, 2));});// Use case: Health check endpoint for monitoring and load balancers// Context: Keep this separate from protected endpoints for deployment health checksapp.get('/health', (_req: Request, res: Response) => {res.json({ status: 'healthy' });});// Security: Validate Bearer tokens on all protected endpoints// Public endpoints (health, metadata) are exempt from authentication// This prevents unauthorized access to MCP tools and operationsapp.use(async (req: Request, res: Response, next: NextFunction) => {// Allow public endpoints without authentication// Use case: Health checks for monitoring; metadata for client discoveryif (req.path === '/.well-known/oauth-protected-resource' || req.path === '/health') {next();return;}// Extract Bearer token from Authorization header// Use case: OAuth 2.1 Bearer token format (RFC 6750)// Security: Reject requests without valid Bearer token prefixconst header = req.headers.authorization;const token = header?.startsWith('Bearer ')? header.slice('Bearer '.length).trim(): undefined;if (!token) {res.status(401).set(WWW_HEADER_KEY, WWW_HEADER_VALUE).json({ error: 'Missing Bearer token' });return;}try {// Validate token using Scalekit SDK// Security: Verifies signature, expiration, issuer, and audience claims// Context: This critical step prevents accepting tokens from other issuersawait scalekit.validateToken(token, { audience: [EXPECTED_AUDIENCE] });next();} catch (error) {res.status(401).set(WWW_HEADER_KEY, WWW_HEADER_VALUE).json({ error: 'Token validation failed' });}});// Handle MCP protocol requests at root path// Use case: Process authenticated MCP tool requests using StreamableHTTPServerTransport// Context: The transport layer handles MCP JSON-RPC communicationapp.post('/', async (req: Request, res: Response) => {const transport = new StreamableHTTPServerTransport({ sessionIdGenerator: undefined });await server.connect(transport);try {await transport.handleRequest(req, res, req.body);} catch (error) {res.status(500).json({ error: 'MCP transport error' });}});// Start the Express serverapp.listen(PORT, () => {console.log(`MCP server running on http://localhost:${PORT}`);}); -
Start the Express server
Section titled “Start the Express server”Start the Express server in development mode with auto-reload enabled. The server will listen on
http://localhost:3002/and display logs indicating Express is ready to receive authenticated MCP requests.Terminal npm run devThe server starts on
http://localhost:3002/and logs indicate Express is ready. The MCP endpoint at/accepts authenticated POST requests, and the metadata endpoint is accessible at/.well-known/oauth-protected-resource. -
Connect with MCP Inspector
Section titled “Connect with MCP Inspector”Test your server end-to-end using the MCP Inspector to verify the OAuth flow works correctly. This allows you to see the authentication handshake and test calling your MCP tools with validated tokens.
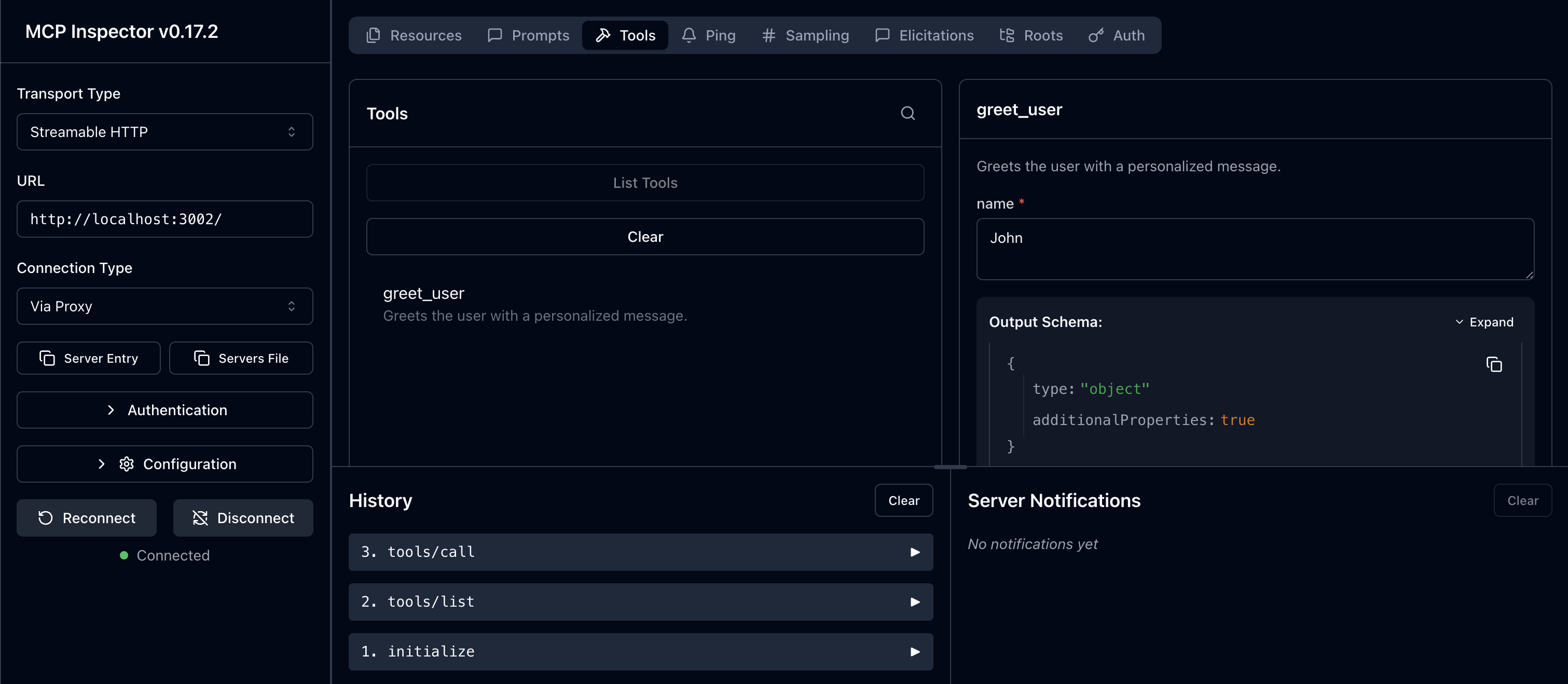
Terminal npx @modelcontextprotocol/inspector@latestIn the Inspector UI:
- Enter your MCP Server URL:
http://localhost:3002/ - Click Connect to initiate the OAuth flow
- Authenticate with Scalekit when prompted
- Run the
greet_usertool with any name
- Enter your MCP Server URL:
You now have a working Express.js MCP server with Scalekit-protected OAuth authentication. Extend this implementation by adding more MCP tools using server.tool() with Zod schema validation, implementing scope-based authorization using custom middleware, integrating with your existing Express application, or adding features like rate limiting and request logging using Express’s middleware ecosystem.