New to MCP?
Lock down MCP connections with OAuth 2.1 so agents get only the access they need
AI systems are moving beyond chatbots to agents that act in the real world. They handle sensitive data and run complex workflows. As they grow, they need a secure, standard way to connect. The Model Context Protocol (MCP) provides that standard. It defines how AI applications safely discover and use external tools and data.
MCP incorporates OAuth 2.1 authorization mechanisms at the transport level. This enables MCP clients to make secure requests to restricted MCP servers on behalf of resource owners.
| Features | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Industry standard | Well-established authorization framework with extensive tooling and ecosystem support |
| Security best practices | Incorporates improvements over OAuth 2.0, removing deprecated flows and enforcing security measures like PKCE |
| Multiple grant types | Supports different use cases: Authorization code for human user scenarios and Client credentials for machine-to-machine integrations |
| Ecosystem compatibility | Integrates with existing identity providers and authorization servers |
MCP authorization specification overview
This authorization mechanism is based on established specifications listed below, but implements a selected subset of their features to ensure security and interoperability while maintaining simplicity:
- OAuth 2.1
- OAuth 2.0 Authorization Server Metadata (RFC8414)
- OAuth 2.0 Dynamic Client Registration Protocol (RFC7591)
- OAuth 2.0 Protected Resource Metadata (RFC9728)
Quick reference: High-level flow
This simplified diagram shows the key actors and main interactions. Use this for quick reference while scrolling through the detailed flow below.
Complete MCP OAuth 2.1 flow
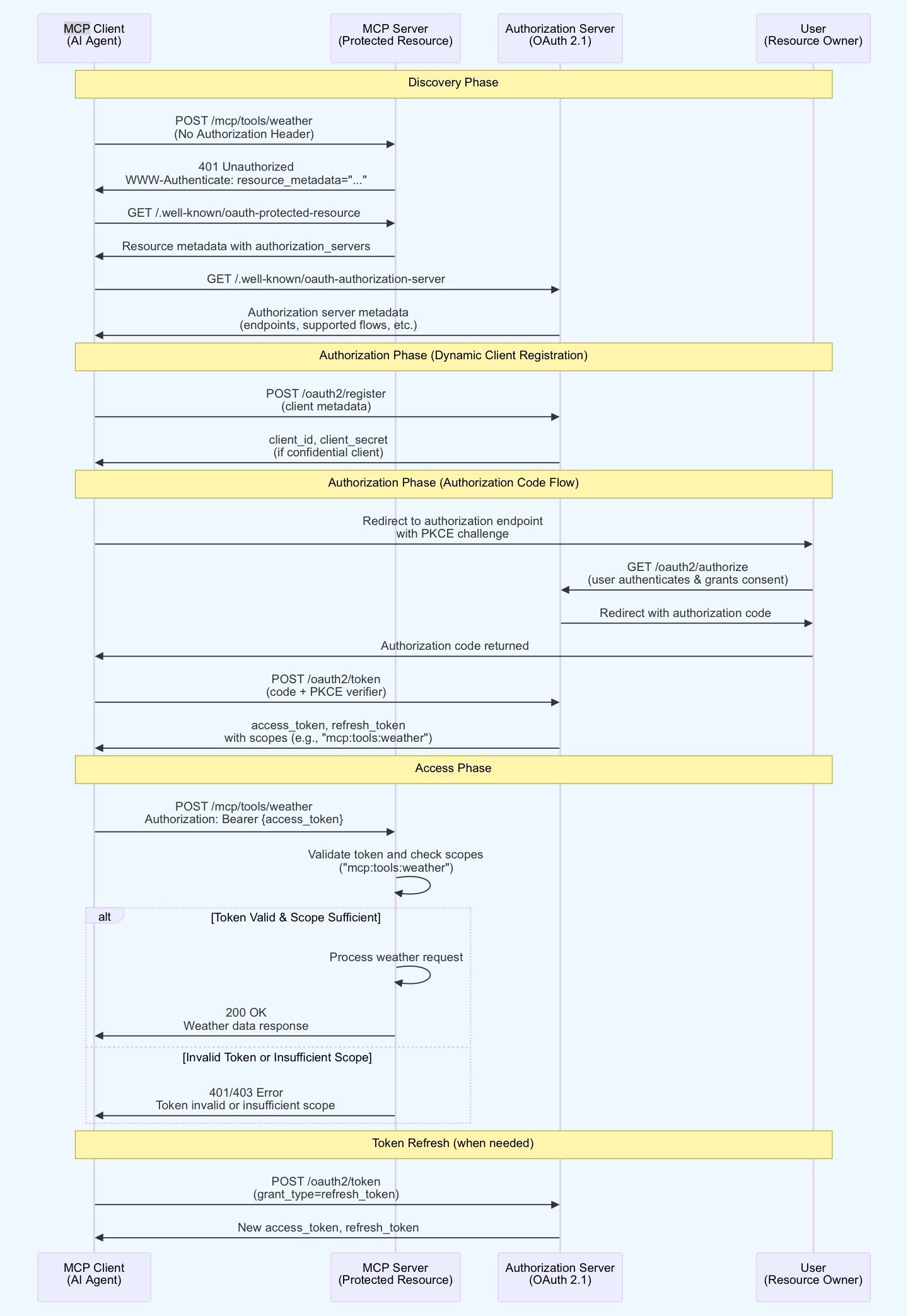
Section titled “Complete MCP OAuth 2.1 flow”Here’s the complete end-to-end authorization flow showing all phases from discovery to token refresh in a single sequence diagram:
Understanding the MCP authorization flow
Section titled “Understanding the MCP authorization flow”Discovery phase
- MCP client attempts to access a protected resource without credentials
- MCP server responds with
401 Unauthorizedand includes authorization metadata in theWWW-Authenticateheader - Client retrieves resource metadata to identify authorization servers
- Client discovers authorization server capabilities through the metadata endpoint
Dynamic client registration
- Client submits registration request with metadata (redirect URIs, application info)
- Authorization server validates the request and issues client credentials
- Client stores credentials securely for subsequent authorization requests
Authorization code flow
- Client generates PKCE code verifier and challenge
- Client redirects user to authorization server with PKCE challenge
- User authenticates and grants consent for requested scopes
- Authorization server redirects back with authorization code
- Client exchanges code and PKCE verifier for access token
- Authorization server validates PKCE and issues tokens with granted scopes
Access phase
- Client includes access token in the Authorization header
- MCP server validates the token signature and expiration
- Server checks if token scopes match the required permissions
- If token is valid and scope is sufficient: Server processes the request and returns 200 OK with the requested data
- If token is invalid or scope is insufficient: Server returns 401 Unauthorized or 403 Forbidden error
Token refresh (when needed)
- Client detects token expiration (through 401 response or token expiry time)
- Client sends refresh token request to authorization server
- Authorization server validates refresh token and issues new access tokens
- Client updates stored tokens and retries the original request
MCP OAuth 2.1 provides secure, standardized authorization for AI agents accessing protected resources. The flow establishes trust, authenticates users, authorizes access, and maintains security throughout the session lifecycle by building each phase on the previous one.
Original diagram reference
For reference, here’s the complete flow diagram showing all phases and interactions in a traditional sequence diagram format: