Automatically assign roles
Automatically assign roles to users in your application by mapping directory provider groups to application roles using Scalekit
Manually assigning roles to users in your application consumes time and creates room for errors for your customers (usually, administrators). Scalekit monitors role changes in connected directories and notifies your application through webhooks. You use the event payload to keep user roles in your application in sync with directory groups in near real time.
How group-based role assignment works
Section titled “How group-based role assignment works”Organization administrators commonly manage varying access levels by grouping users in their directory. For example, to manage access levels to GitHub, they create groups for each role and assign users to those groups. In this case a Maintainer group includes all the users who should have maintainer access to the repository.
This enables your application to take necessary actions such as creating or modifying user roles as directed by the organization’s administrators.
Set up automatic role assignment
Section titled “Set up automatic role assignment”To enable administrators to map directory groups to roles in your app, complete these steps:
- Open the Scalekit dashboard.
- Go to Roles & Permissions.
- Use the Roles and Permissions sections to configure your application’s authorization model.
- Register your app’s roles and permissions so Scalekit can reference them in mappings and webhook events.
Select Add role to create a new role.
Choose clear display names and descriptions for your roles. This helps customers understand and align the roles with the access levels they already maintain in their directory.
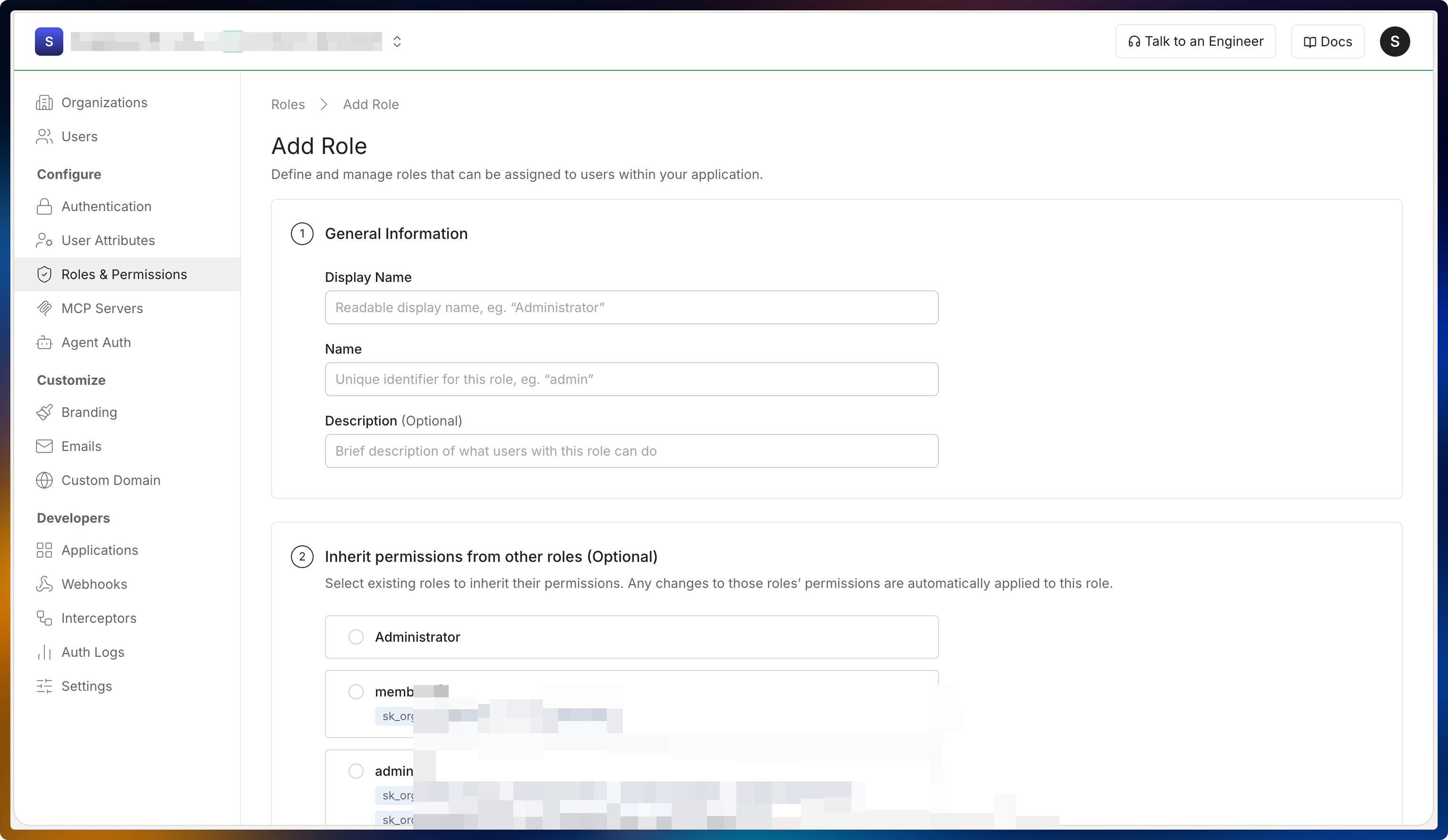
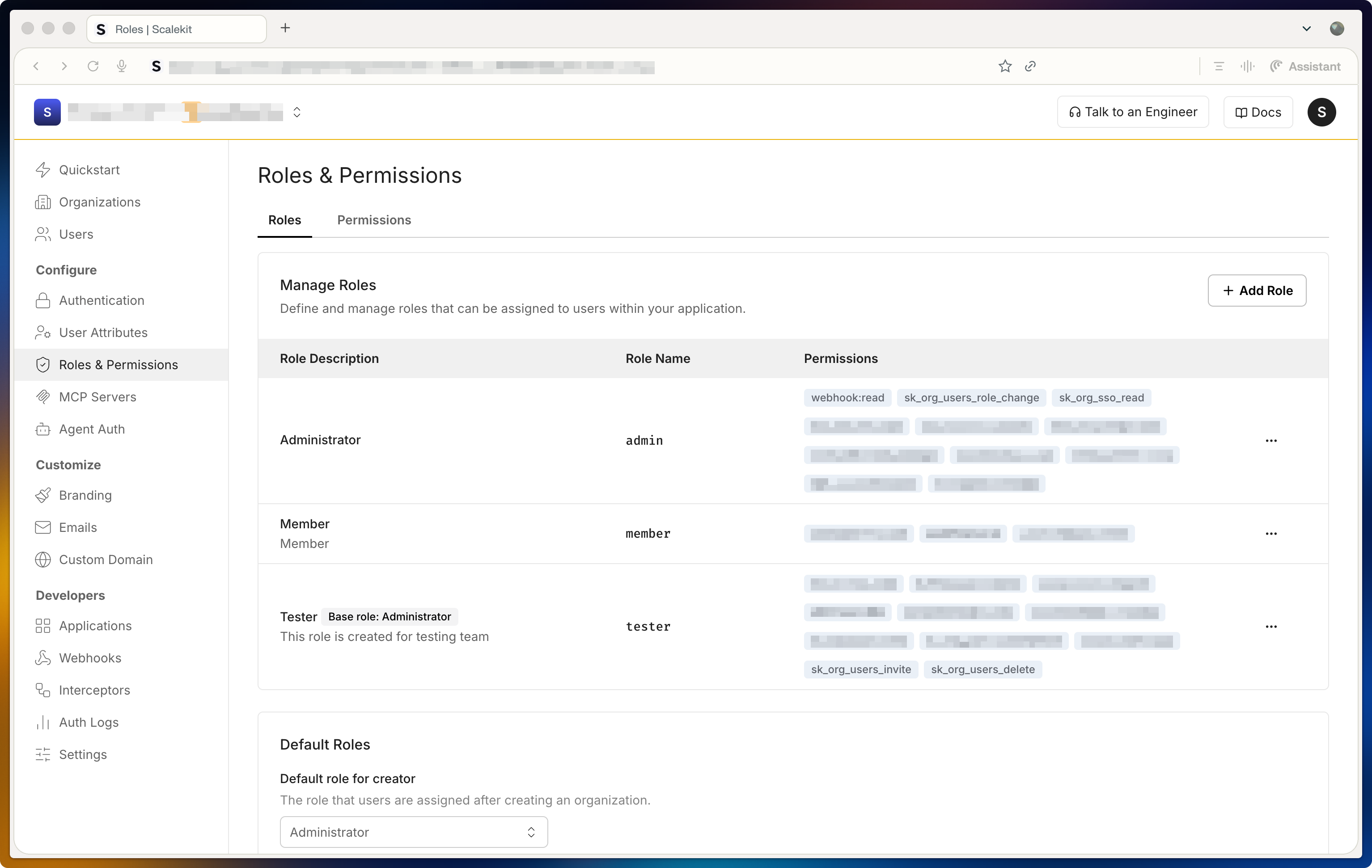
The roles page lists a couple of sample roles by default. You can edit or remove these and add new roles that match your application’s authorization model.
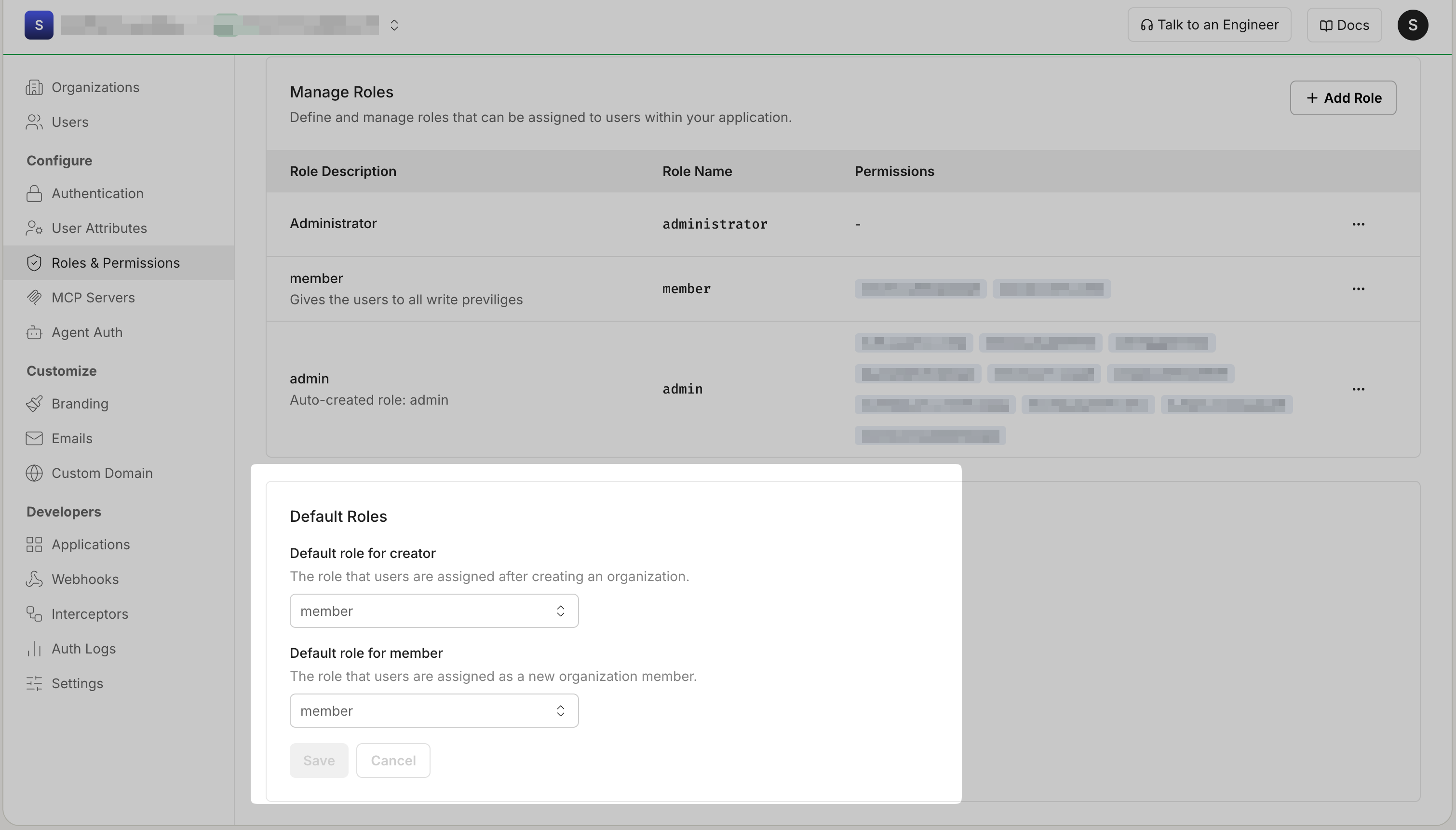
Specify the default roles your app wants to assign to the organization creator and to members who belong to the same organization. All added roles are available for you to select as default roles.
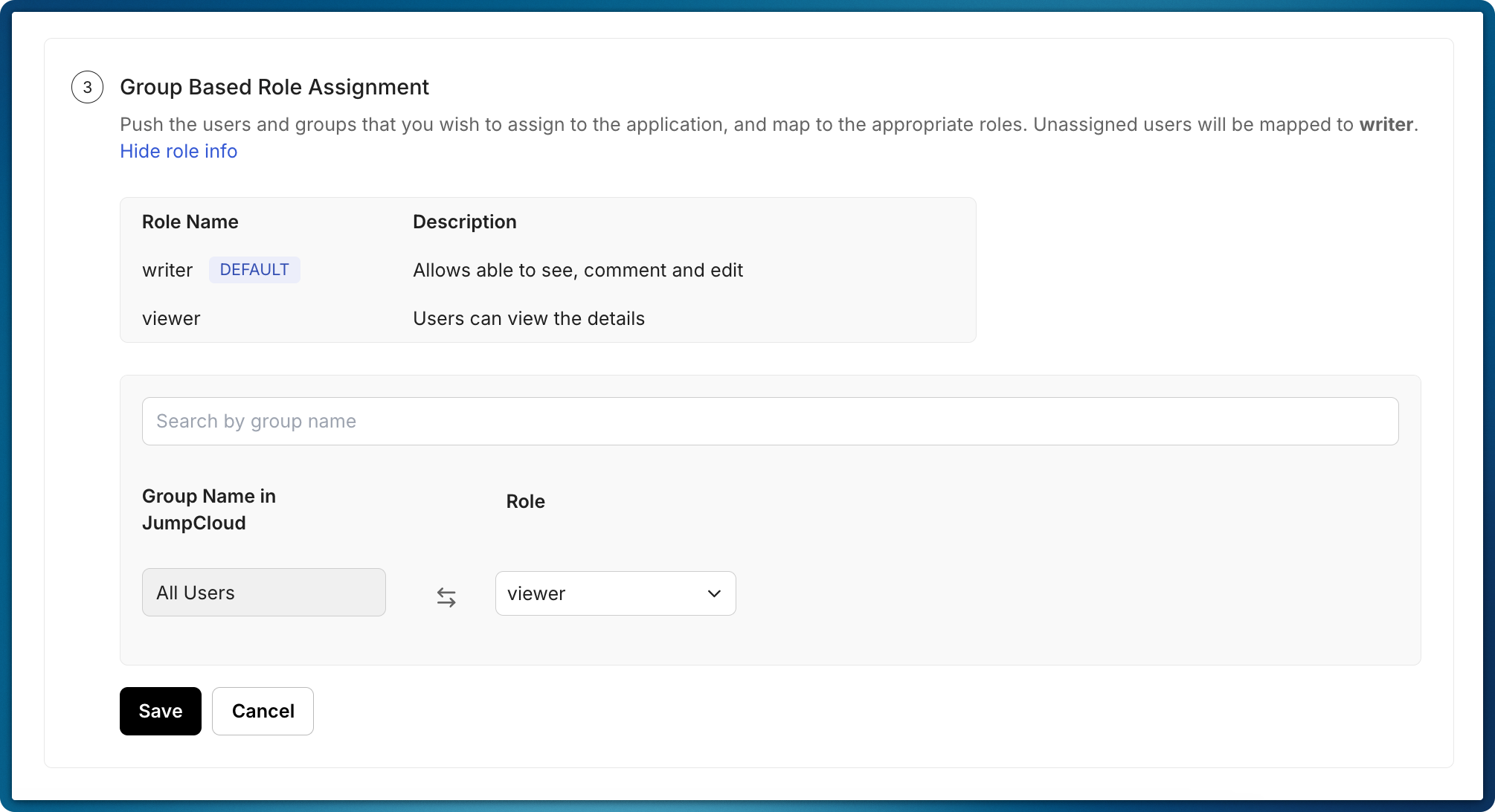
Connect organization groups to app roles
Section titled “Connect organization groups to app roles”After you create roles, they represent the roles in your app that you want directory groups to control. Users receive role assignments in your app based on the groups they belong to in their directory.
You can set up this mapping in two ways:
- Configure mappings in the Scalekit dashboard on behalf of organization administrators. Select the organization and go to the SCIM provisioning tab.
- Share the admin portal link with organization administrators so they can configure the mappings themselves.
Scalekit automatically displays mapping options in both the Scalekit dashboard and the admin portal. This allows administrators to connect organization groups to app roles without custom logic in your application.
Handle role update events
Section titled “Handle role update events”Scalekit continuously monitors updates from your customers’ directory providers and sends event payloads to your application through a registered webhook endpoint. To set up these endpoints and manage subscriptions, use the Webhooks option in the Scalekit dashboard.
Listen for the organization.directory.user_updated event to determine a user’s roles from the payload. Scalekit automatically includes role information that is relevant to your app, based on the roles you configured in the Scalekit dashboard.
// Webhook endpoint to receive directory role updatesapp.post('/webhook', async (req, res) => { // Extract event data from the webhook payload const event = req.body; const { email, roles } = event.data;
console.log('Received directory role update for:', email);
// Extract role_name from the roles array, if present const roleName = Array.isArray(roles) && roles.length > 0 ? roles[0].role_name : null; console.log('Role name received:', roleName);
// Business logic: update user role and permissions in your app if (roleName) { await assignRole(roleName, email); console.log('Updated access for user:', email); }
res.status(201).json({ message: 'Role processed', });});import jsonfrom fastapi import FastAPI, Requestfrom fastapi.responses import JSONResponse
app = FastAPI()
@app.post("/webhook")async def api_webhook(request: Request): # Parse request body from the webhook payload body = await request.body() payload = json.loads(body.decode())
# Extract user data user_roles = payload["data"].get("roles", []) user_email = payload["data"].get("email")
print("User roles:", user_roles) print("User email:", user_email)
# Business logic: assign role in your app if user_roles and user_email: await assign_role(user_roles[0], user_email)
return JSONResponse( status_code=201, content={"message": "Role processed"}, )@PostMapping("/webhook")public ResponseEntity<Map<String, String>> webhook(@RequestBody String body, @RequestHeader Map<String, String> headers) { ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
try { JsonNode node = mapper.readTree(body); JsonNode roles = node.get("data").get("roles"); String email = node.get("data").get("email").asText();
System.out.println("Roles: " + roles); System.out.println("Email: " + email);
// TODO: Add role to user in your application
Map<String, String> responseBody = new HashMap<>(); responseBody.put("message", "Role processed"); return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.CREATED).body(responseBody); } catch (IOException e) { return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST).build(); }}mux.HandleFunc("POST /webhook", func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) { // Read request body from the webhook payload bodyBytes, err := io.ReadAll(r.Body) if err != nil { http.Error(w, err.Error(), http.StatusBadRequest) return }
// Parse webhook payload var body struct { Data map[string]interface{} `json:"data"` }
if err := json.Unmarshal(bodyBytes, &body); err != nil { http.Error(w, err.Error(), http.StatusBadRequest) return }
// Extract user data roles, _ := body.Data["roles"] email, _ := body.Data["email"]
fmt.Println("Roles:", roles) fmt.Println("Email:", email)
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusCreated) _, _ = w.Write([]byte(`{"message":"Role processed"}`))})Refer to the list of directory webhook events you can subscribe to for more event types.