FastMCP quickstart
FastMCP todo server with OAuth scope validation and CRUD operations.
This guide shows you how to build a production-ready FastMCP server protected by Scalekit’s OAuth authentication. You’ll register your server as a protected resource, implement scope-based authorization for CRUD operations, and validate tokens on every request.
Use this quickstart to experience a working reference implementation with a simple todo application. The todo app demonstrates how to enforce todo:read and todo:write scopes across multiple tools. After completing this guide, you can apply the same authentication pattern to secure your own FastMCP tools. The full code is available on GitHub.
Prerequisites
- A Scalekit account with permission to manage MCP servers
- Python 3.11+ installed locally
- Familiarity with OAuth scopes and basic terminal commands
Review the FastMCP authorization flow
-
Register your MCP server in Scalekit
Section titled “Register your MCP server in Scalekit”Create a protected resource entry so Scalekit can issue scoped tokens that FastMCP validates on every request.
- Navigate to Dashboard > MCP Servers > Add MCP Server.
- Enter a descriptive name (for example,
FastMCP Todo Server). - Set Server URL to
http://localhost:3002/(keep the trailing slash). This field is a required.
For a server running athttp://localhost:3002/mcp, registerhttp://localhost:3002/. FastMCP appends/mcpautomatically, so always provide the base URL with a trailing slash. - Create or link the scopes below, then click Save.
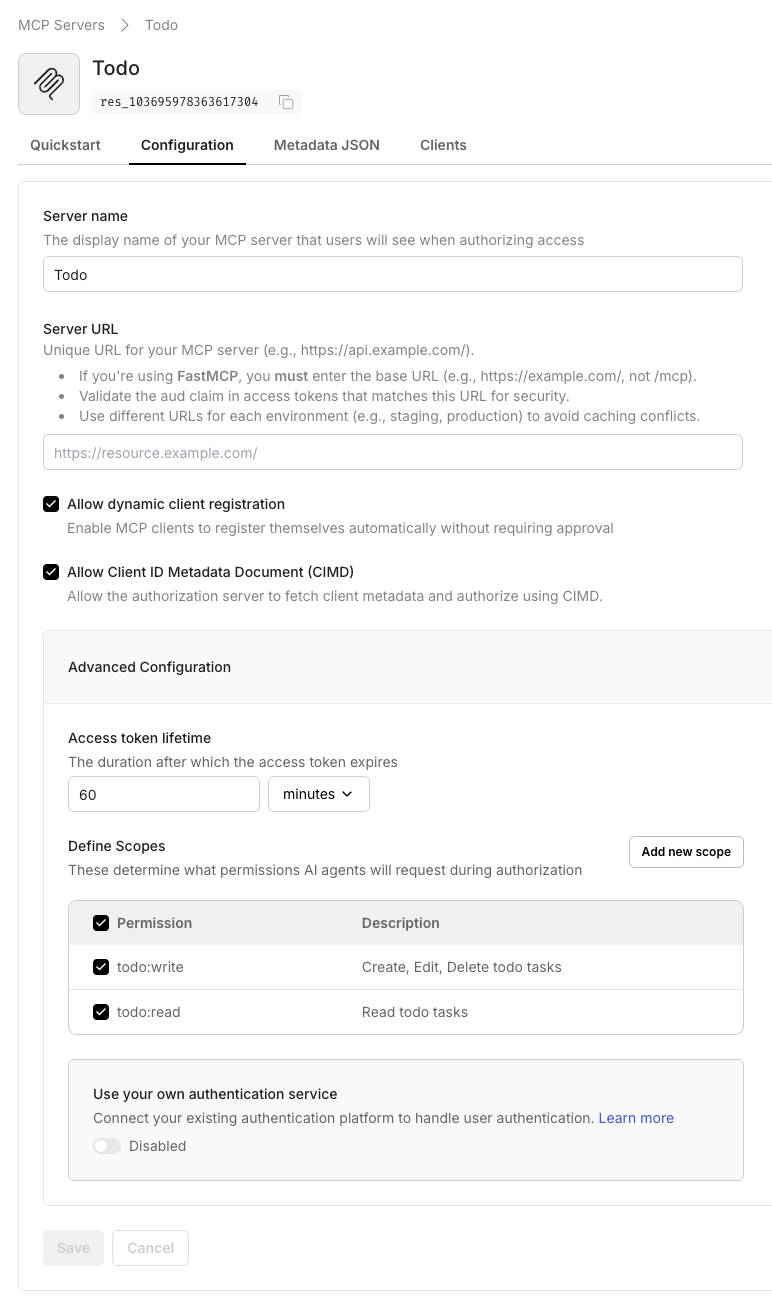
Scope Description Required todo:readGrants read access to todo tasks Yes todo:writeAllows creating, updating, or deleting tasks Yes -
Create your FastMCP todo server
Section titled “Create your FastMCP todo server”Prepare a fresh directory and virtual environment to keep FastMCP dependencies isolated.
Terminal mkdir -p fastmcp-todocd fastmcp-todopython3 -m venv venvsource venv/bin/activate -
Add dependencies and configuration templates
Section titled “Add dependencies and configuration templates”Create the support files that FastMCP and Scalekit expect, then install the required libraries.
Terminal cat <<'EOF' > requirements.txtfastmcp>=2.13.0.2python-dotenv>=1.0.0EOFpip install -r requirements.txtcat <<'EOF' > env.examplePORT=3002SCALEKIT_ENVIRONMENT_URL=https://your-environment-url.scalekit.comSCALEKIT_CLIENT_ID=your_client_idSCALEKIT_RESOURCE_ID=mcp_server_idMCP_URL=http://localhost:3002/EOF -
Implement the FastMCP todo server
Section titled “Implement the FastMCP todo server”Copy the following code into
server.py. It registers the Scalekit provider, defines an in-memory todo store, and exposes CRUD tools guarded by OAuth scopes.server.py 15 collapsed lines"""Scalekit-authenticated FastMCP server providing in-memory CRUD tools for todos.This example demonstrates how to protect FastMCP tools with OAuth scopes.Each tool validates the required scope before executing operations."""import osimport uuidfrom dataclasses import dataclass, asdictfrom typing import Optionalfrom dotenv import load_dotenvfrom fastmcp import FastMCPfrom fastmcp.server.auth.providers.scalekit import ScalekitProviderfrom fastmcp.server.dependencies import AccessToken, get_access_tokenload_dotenv()# Use case: Configure FastMCP server with OAuth protection# Security: Scalekit provider validates every request's Bearer tokenmcp = FastMCP("Todo Server",stateless_http=True,auth=ScalekitProvider(environment_url=os.getenv("SCALEKIT_ENVIRONMENT_URL"),client_id=os.getenv("SCALEKIT_CLIENT_ID"),resource_id=os.getenv("SCALEKIT_RESOURCE_ID"),# FastMCP appends /mcp automatically; keep base URL with trailing slash onlymcp_url=os.getenv("MCP_URL"),),)@dataclassclass TodoItem:id: strtitle: strdescription: Optional[str]completed: bool = Falsedef to_dict(self) -> dict:return asdict(self)# Use case: In-memory storage for demo purposes# Production: Replace with your database or persistent storage_TODO_STORE: dict[str, TodoItem] = {}def _require_scope(scope: str) -> Optional[str]:"""Security: Validate that the current request's token includes the required scope.This prevents unauthorized access to protected operations."""token: AccessToken = get_access_token()if scope not in token.scopes:return f"Insufficient permissions: `{scope}` scope required."return None@mcp.tooldef create_todo(title: str, description: Optional[str] = None) -> dict:"""Use case: Create a new todo item for task trackingRequires: todo:write scope"""error = _require_scope("todo:write")if error:return {"error": error}todo = TodoItem(id=str(uuid.uuid4()), title=title, description=description)_TODO_STORE[todo.id] = todoreturn {"todo": todo.to_dict()}@mcp.tooldef list_todos(completed: Optional[bool] = None) -> dict:"""Use case: Retrieve all todos, optionally filtered by completion statusRequires: todo:read scope"""error = _require_scope("todo:read")if error:return {"error": error}todos = [todo.to_dict()for todo in _TODO_STORE.values()if completed is None or todo.completed == completed]return {"todos": todos}@mcp.tooldef get_todo(todo_id: str) -> dict:"""Use case: Retrieve a specific todo by IDRequires: todo:read scope"""error = _require_scope("todo:read")if error:return {"error": error}todo = _TODO_STORE.get(todo_id)if todo is None:return {"error": f"Todo `{todo_id}` not found."}return {"todo": todo.to_dict()}@mcp.tooldef update_todo(todo_id: str,title: Optional[str] = None,description: Optional[str] = None,completed: Optional[bool] = None,) -> dict:"""Use case: Update existing todo properties or mark as completeRequires: todo:write scope"""error = _require_scope("todo:write")if error:return {"error": error}todo = _TODO_STORE.get(todo_id)if todo is None:return {"error": f"Todo `{todo_id}` not found."}if title is not None:todo.title = titleif description is not None:todo.description = descriptionif completed is not None:todo.completed = completedreturn {"todo": todo.to_dict()}@mcp.tooldef delete_todo(todo_id: str) -> dict:"""Use case: Remove a todo from the systemRequires: todo:write scope"""error = _require_scope("todo:write")if error:return {"error": error}todo = _TODO_STORE.pop(todo_id, None)if todo is None:return {"error": f"Todo `{todo_id}` not found."}return {"deleted": todo_id}if __name__ == "__main__":# Start HTTP transport servermcp.run(transport="http", port=int(os.getenv("PORT", "3002"))) -
Provide runtime secrets
Section titled “Provide runtime secrets”Copy the environment template and populate the values from your Scalekit dashboard.
Terminal cp env.example .envopen .envVariable Description SCALEKIT_ENVIRONMENT_URLYour Scalekit environment URL from Dashboard > Settings SCALEKIT_CLIENT_IDClient ID from Dashboard > Settings SCALEKIT_RESOURCE_IDThe resource identifier assigned to your MCP server (starts with res_)MCP_URLThe base public URL you registered (keep trailing slash, e.g., http://localhost:3002/)PORTLocal port for FastMCP HTTP transport (defaults to 3002) -
Run the FastMCP server locally
Section titled “Run the FastMCP server locally”Start the server so it can accept authenticated MCP requests at
/mcp.Terminal source venv/bin/activatepython server.pyWhen the server boots successfully, you’ll see FastMCP announce the HTTP transport and listen on
http://localhost:3002/, ready to enforce Scalekit-issued tokens.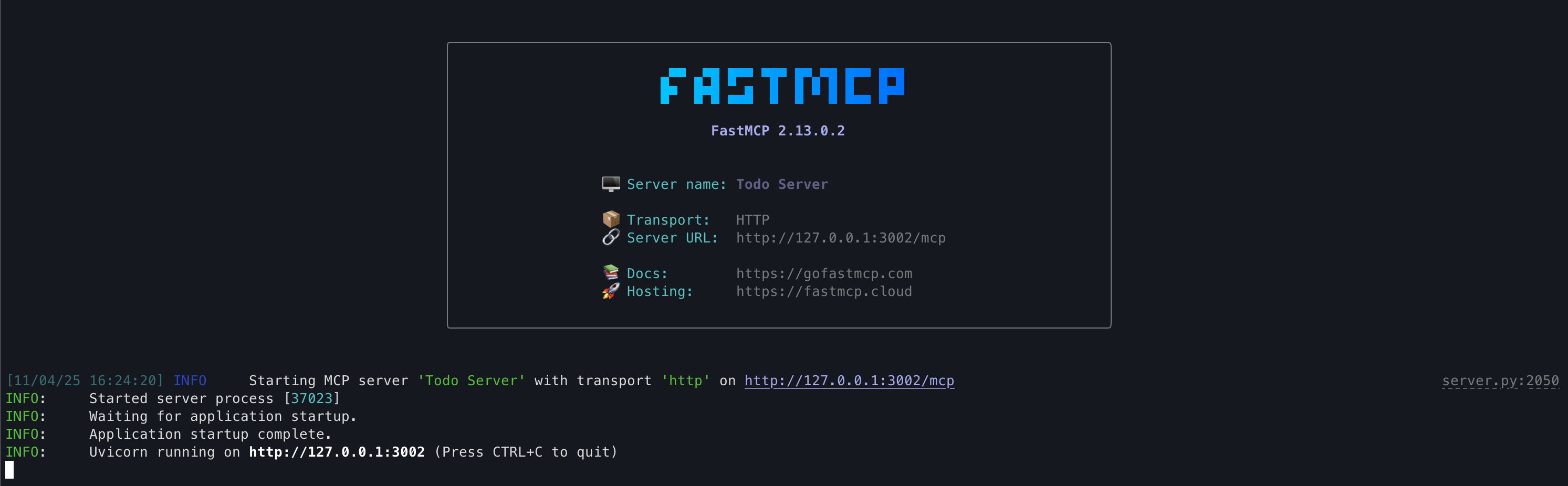
-
Connect with an MCP client
Section titled “Connect with an MCP client”Use any MCP-compatible client to exercise the todo tools with scoped tokens. During development, the MCP Inspector demonstrates how the Scalekit provider enforces scopes end-to-end.
Terminal npx @modelcontextprotocol/inspector@latestIn the Inspector UI, point the client to
http://localhost:3002/mcpand click Connect. The client initiates OAuth authentication with Scalekit. After successful authentication, run any tool—the server exposescreate_todo,list_todos,get_todo,update_todo, anddelete_todo.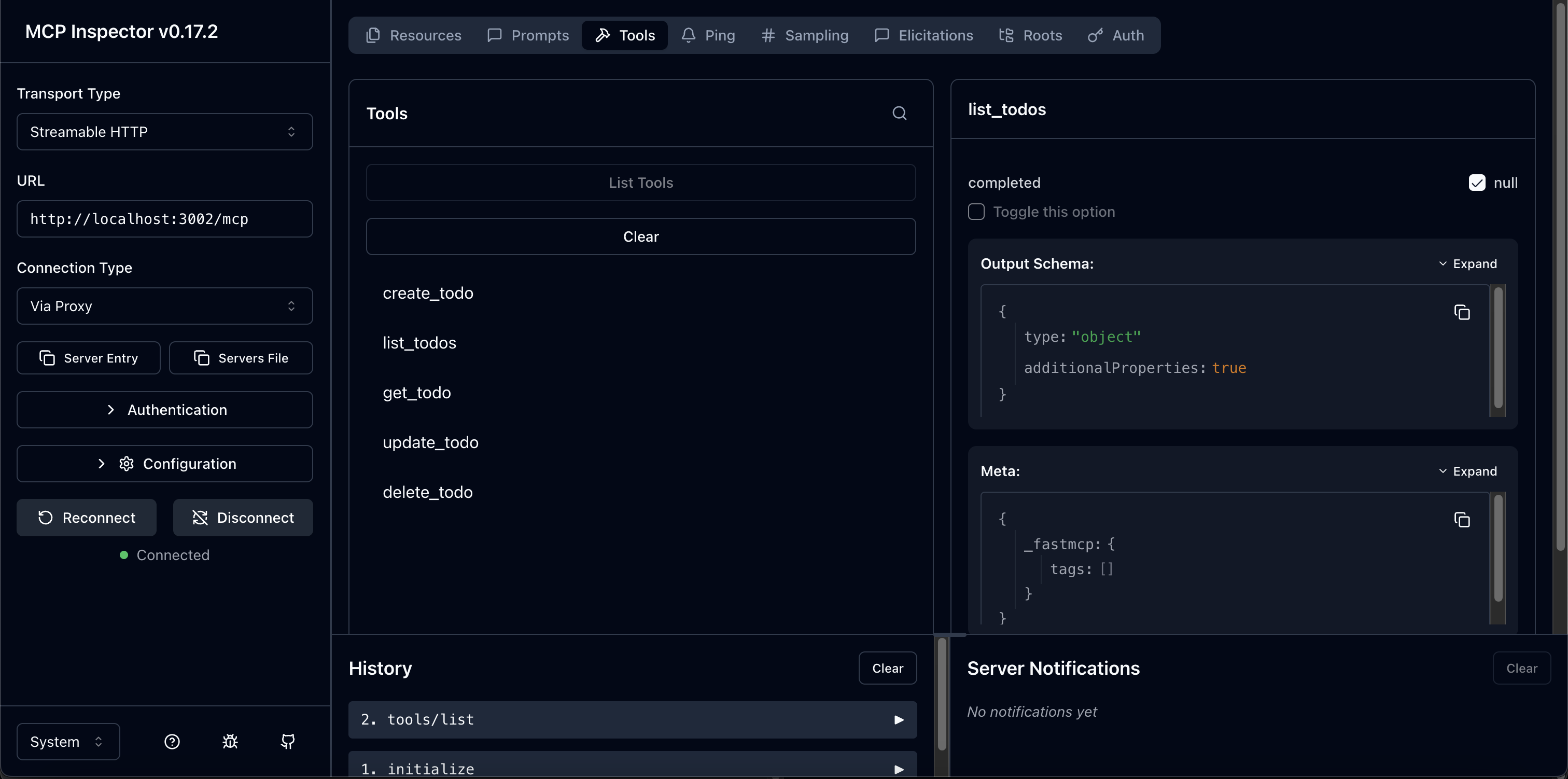
Once you’re satisfied with the quickstart example, extend server.py with your own FastMCP tools or replace the in-memory store with your production data source. Scalekit’s provider handles authentication for any toolset you add.